
The prevalence of cardiovascular diseases and stroke is globally increasing. However, there are some evidence that cardiac rehabilitation delivers the adequate health benefits to the patients concerned, offering a better and healthier lifestyle. Cardiac rehabilitation is a medically supervised program comprising of exercises and informatory sessions for patients diagnosed with heart disease. These sessions are extremely informative which include elements of health education, learning of physical exercises, stress management, and advice on cardiovascular risk reduction. Furthermore, the cardiac rehabilitation programs also include sessions on primary health education and psychological counseling.
It has been observed that most patients suffering from coronary diseases aren't aware of these sessions that take place on a regular basis at conferences, hospitals, etc. enabling them to lead a healthier life. Therefore, it is also the duty of clinicians to endorse cardiac rehabilitation to individuals who have been diagnosed with a coronary ailment.
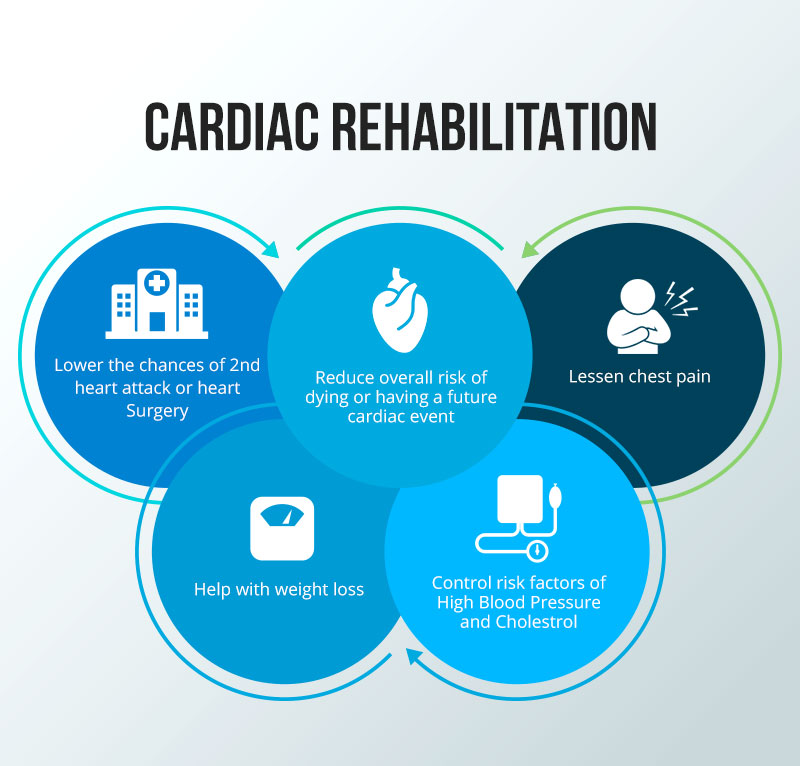
Effective implementation of cardiac rehabilitation after the diagnosis of heart diseases ensures improved mortality rate, reduced frequency of hospitalization, and betterment in psychological wellbeing. Moreover, a cardiac rehab program helps you to:
A cardiac rehab begins as soon as you are hospitalized for a heart surgery or treatment, or soon after you've had a stroke. The ideal program consists of following 4 phases:
Phase 1: It is an in-patient phase in the hospital, also called recuperation phase, which generally lasts up to 6 weeks in which a patient receives help in a range of motion activities, intermittent standing or sitting, and walking. The phase aims at reducing the de-conditioning that normally co-occur with prolonged bed rest.
Phase 2: It is an outpatient phase that commences immediately upon phase 1 and lasts up to 4-6 weeks in which exercise bouts are of short duration and low intensity. The patient begins with activities of equal strength as normal daily activities.
Phase 3: Also called a long-term conditioning phase, the patient progresses and reaches to a more advanced exercise program during the phase.
Phase 4: Also known as maintenance phase, the patient enters after 4 to 6 months following the commencement of the cardiac rehab program.
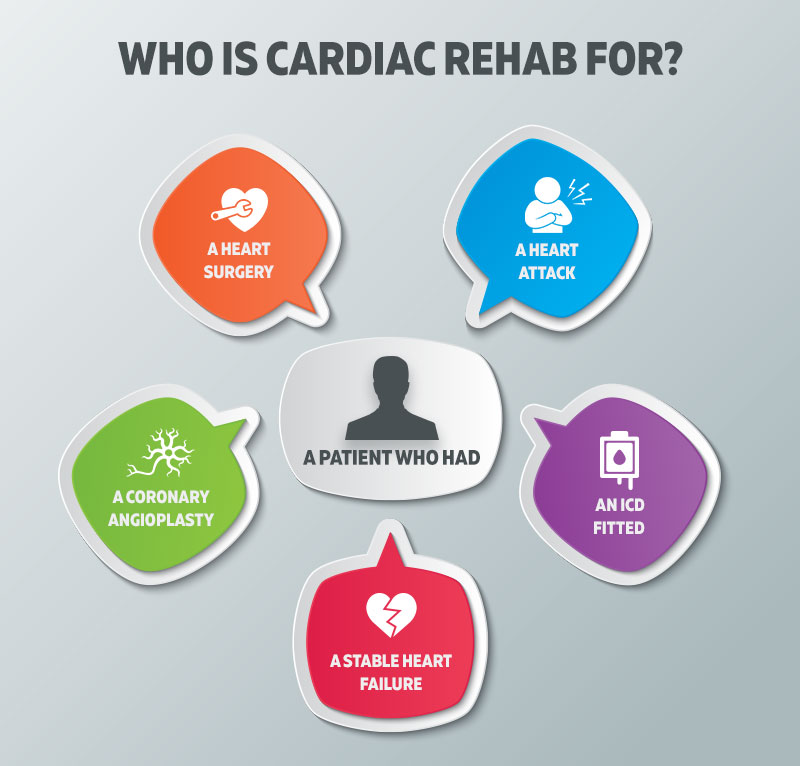
A cardiac rehab program is designed for patients newly diagnosed with a heart issue, or patients with a heart transplant, or acute coronary syndrome, or ventricular assist device, or confirmed with the diagnosis of exertional angina, heart valve replacements, or patients who have undergone surgery for implantation of an intra-cardiac defibrillator. The patient's cardiac rehab program depends upon the health disorder and medical history. Therefore, the rehab team will take the patient's medical history into keen consideration, do a physical exam, and perform various tests before starting the program. Possible tests may include cardiac imaging tests, electrocardiogram (EKG), and a stationary bike or treadmill exercise test. The patient may also have tests to measure the blood sugar and cholesterol levels. During cardiac rehab, the patient learns to perform exercises safely and increases the daily physical activity day by day. The period that the patient spends in cardiac rehab program depends on the condition's nature and its intensity.
Cardiac Rehabilitation is a secondary prevention program recognized as integral to the overall wellbeing and care of patients with stroke or cardiovascular issue. The program usually comprises of following basic elements:
Health behavior education is often synonymously used with different aspects of lifestyle directly related to overall health, life expectancy and a heart condition. Guidance regarding nutrition, training on physical activities and exercise, and education on factors causing cardiovascular issues can help a patient improve overall lifestyle and alleviate the symptoms of the health disorder.
Physical Activity And Exercise: Physical activity has various physical, psychological and emotional health benefits that can be from supervised activities to a daily walk in the park. When it comes to cardiac rehabilitation, a physiotherapist helps you perform physical activities and exercises under its keep supervision. The idea is mainly to get moving, and the physical exercises primarily deliver following benefits:
Diet: Adopting a heart-healthy diet that includes a meal with low in salt and rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, low-fat meat, and fish. Choice of right foods aimed at reducing fat, cholesterol level and sodium in your diet are beneficiary for heart patients. A health nutritionist or dietitian can help you develop a better diet plan meeting your health needs.
Smoking cessation: Smoking injures nearly every organ of your body, including your heart. Most of the cardiac rehab programs offer practical methods to help patients kick off the harmful habit.
Cardiac patients often experience anxiety and depression causing reduced quality of life and mortality. Therefore, cardiac rehab program incorporates the mental and psychological treatments for stress and anxiety.
Diabetes, high cholesterol, hypertension, blood circulation issues, atrial fibrillation, and obesity are leading medical risk factors to a stroke. Therefore, cardiac rehab team helps patients be able to manage such factors if they are already affected by them.
The rehab team aims for a long term treatment and healing within the heart by helping patients improve their lifestyle, avoid risk factors, become habitual of doing daily exercises, and prefer healthy foods.
To prevent a problem is far easier than to solve it. Similarly, cardioprotective therapies aim at preventing the recurrence of a cardiovascular issue, which are the combination of above-described cardiac rehab elements.
Initial and ongoing medical evaluation helps the cardiac team determine physical abilities and limitations, and other conditions, and keep track of the progress over time. During the assessment, the healthcare team looks at different risk factors for heart disorder or stroke. It helps them tailor the program to each individual situation, ensuring safety and effectiveness.
Delivery of services mentioned above requires expertise from a range of different specialists and professionals. The team may include a cardiologist, community cardiologist, nurse specialist, physician, physiotherapist, a general practitioner with a special interest, nutritionist, psychologist, occupational therapist, clerical administrator, and exercise specialist.
Despite the documented proof of the benefits associated with a cardiac rehabilitation in enhancing recovery, reducing mortality and improving overall health following a heart surgery or stroke, just nearly one-third of the patients participate in such programs. Mentioned below are some of the barriers to cardiac rehab participation: